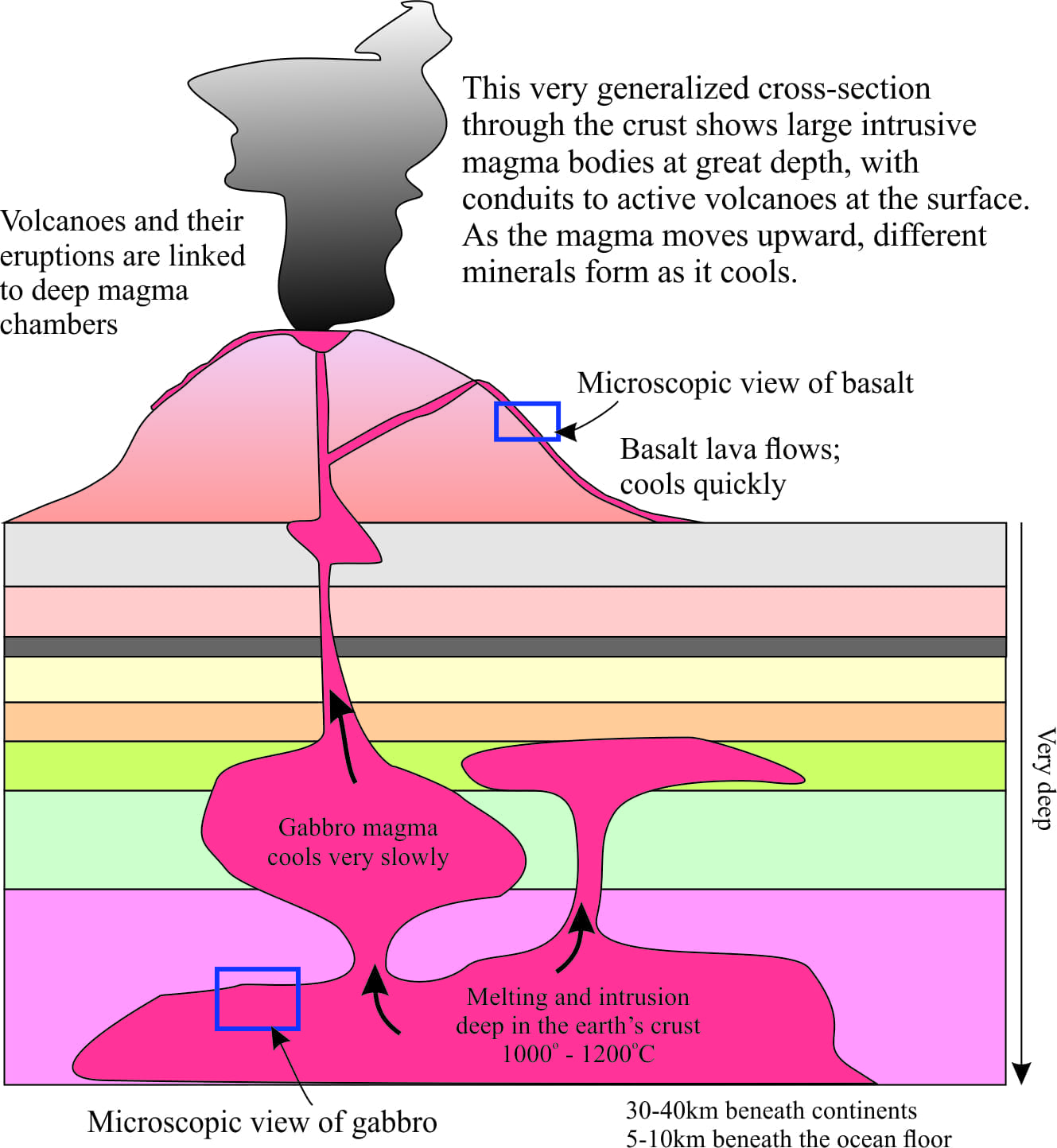
How Is Gabbro Formed - It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive.
Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the.
It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive.
Image Result For Rock Chart Igneous Rock Igneous Rock Igneous Rock
Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive.
Pagina G (Termos)
It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive.
Gabbro Igneous rocks
Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface.
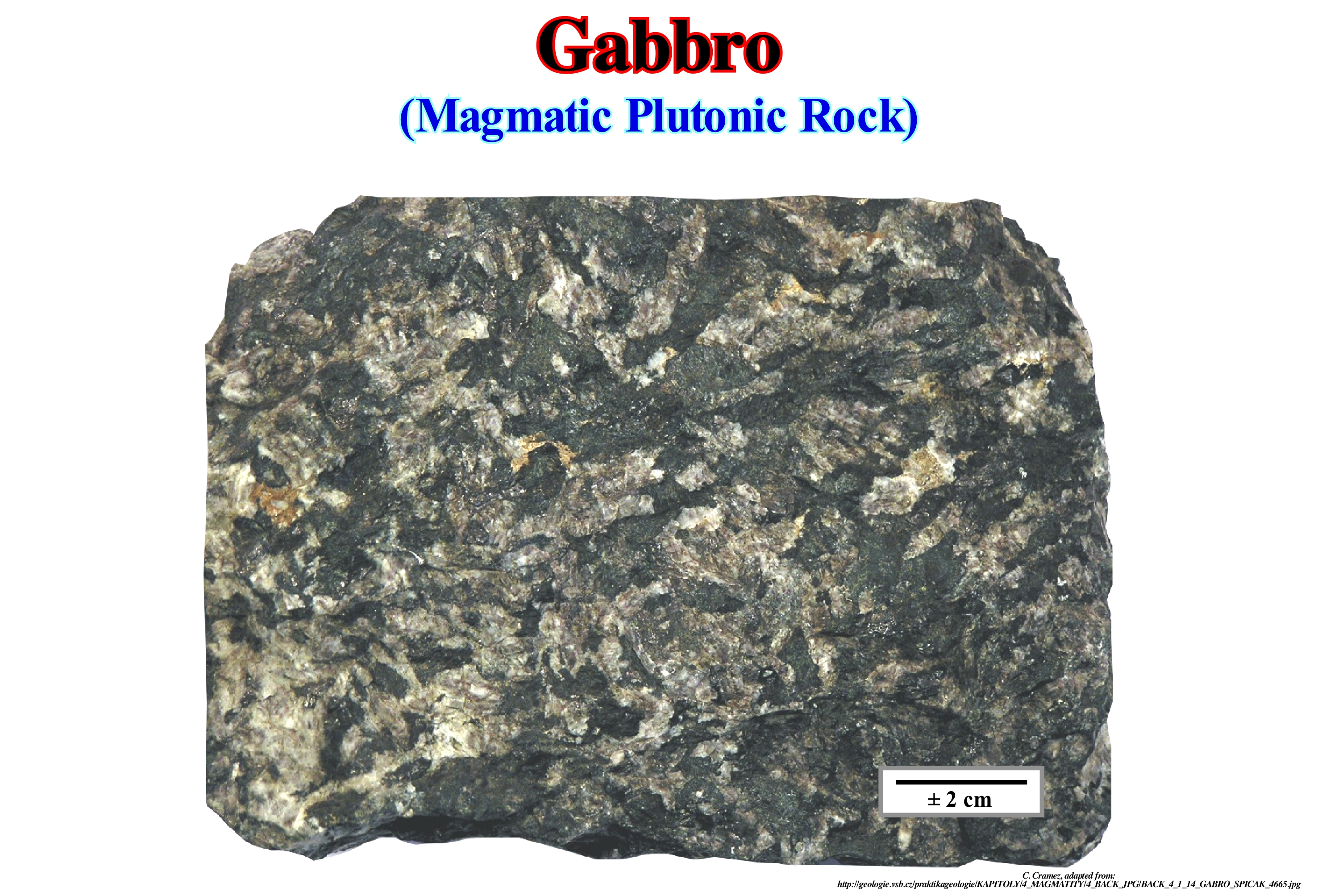
Gabbro Properties, Formation, Composition, Uses
Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface.
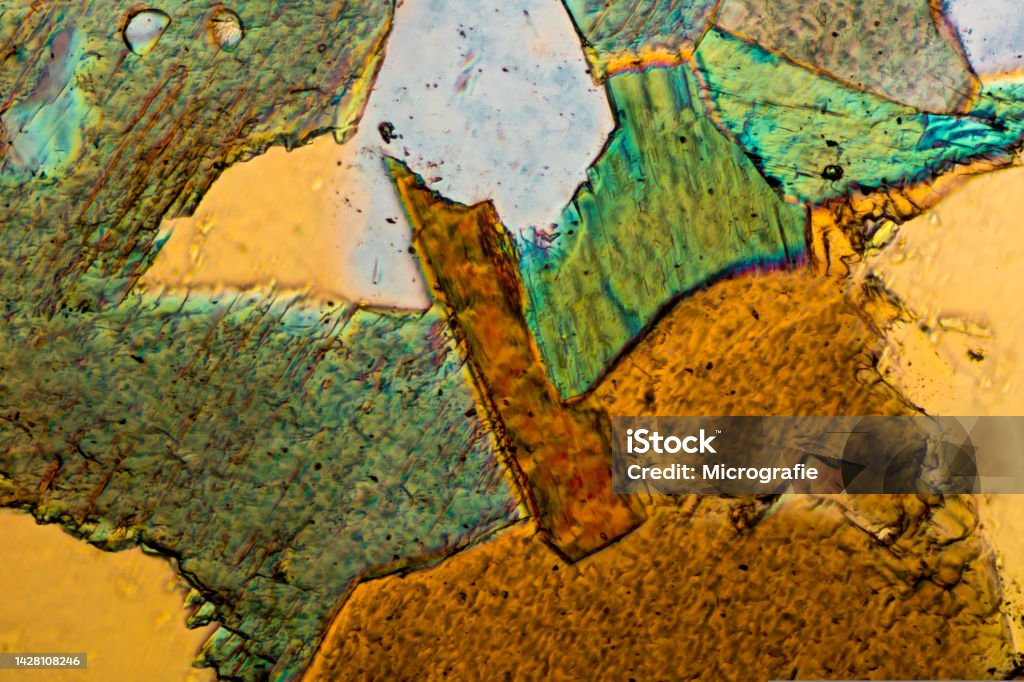
Crosssection Of Gabbro Photographed Through The Microscope In Polarized
Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive.
Crosssection Of Gabbro Photographed Through The Microscope In Polarized
Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the.
Field photograph of syntectonic gabbro. (a) Sharp contact between
Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive.
Hand sample photographs of (a) fine‐grained gabbro crosscut by diffuse
Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface.
Learning Geology Gabbro
Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive. It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface.
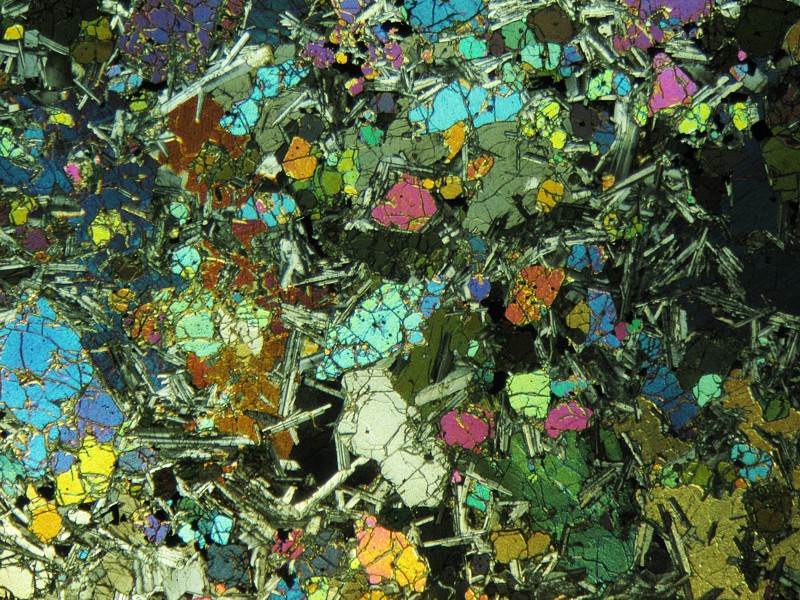
Sliced thin; time and process recorded in igneous rocks Geological
It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Essentially, gabbro is the intrusive. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface.
Essentially, Gabbro Is The Intrusive.
It is usually black or dark green in color and composed mainly of the. Gabbro is the intrusive equivalent of basalt, which is its extrusive counterpart formed from the same type of magma but cooled rapidly at the surface.