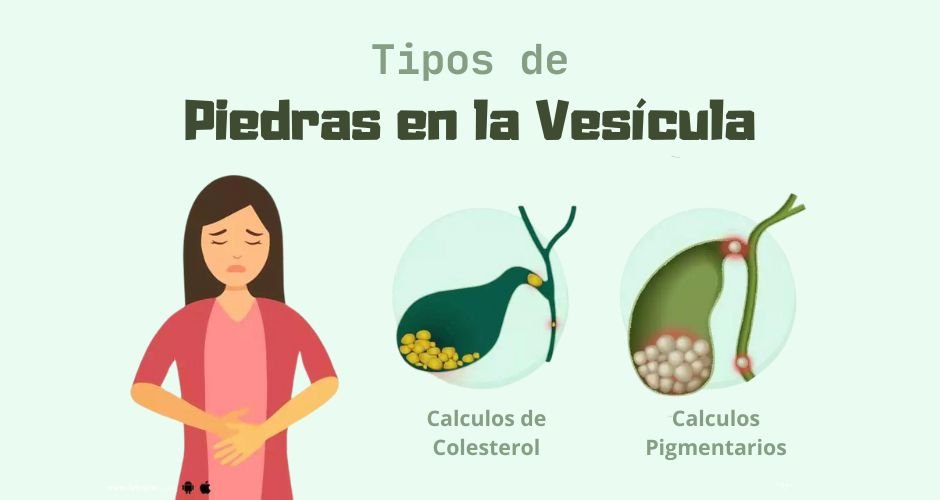
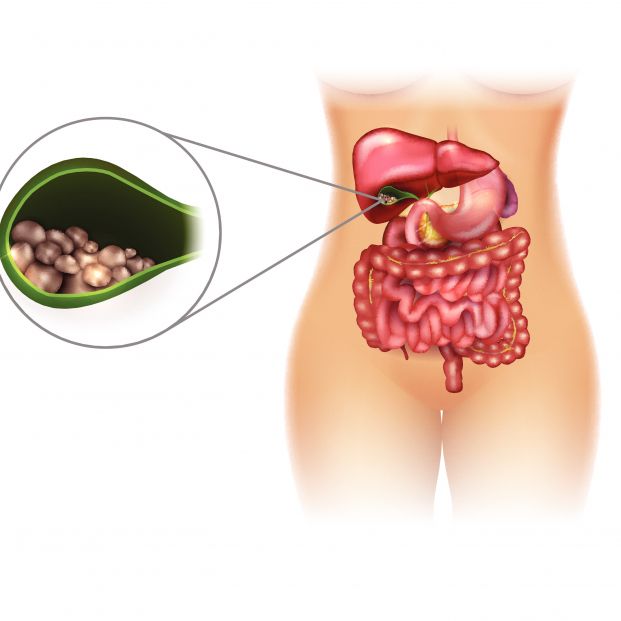
Por Qué Se Forman Piedras En La Vesícula - Several years ago when i completed about half a. Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. I have 2 matrices and have been trying to multiply them but to no avail. Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. Because of that, multiplication and. Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$.
Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$. Because of that, multiplication and. Several years ago when i completed about half a. Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. I have 2 matrices and have been trying to multiply them but to no avail. The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k!
Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! Because of that, multiplication and. António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. Several years ago when i completed about half a. I have 2 matrices and have been trying to multiply them but to no avail.
Por Que Se Forman Los Calculos En La Vesicula Form example download
António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. Several years ago when i completed about half a. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. Otherwise this.
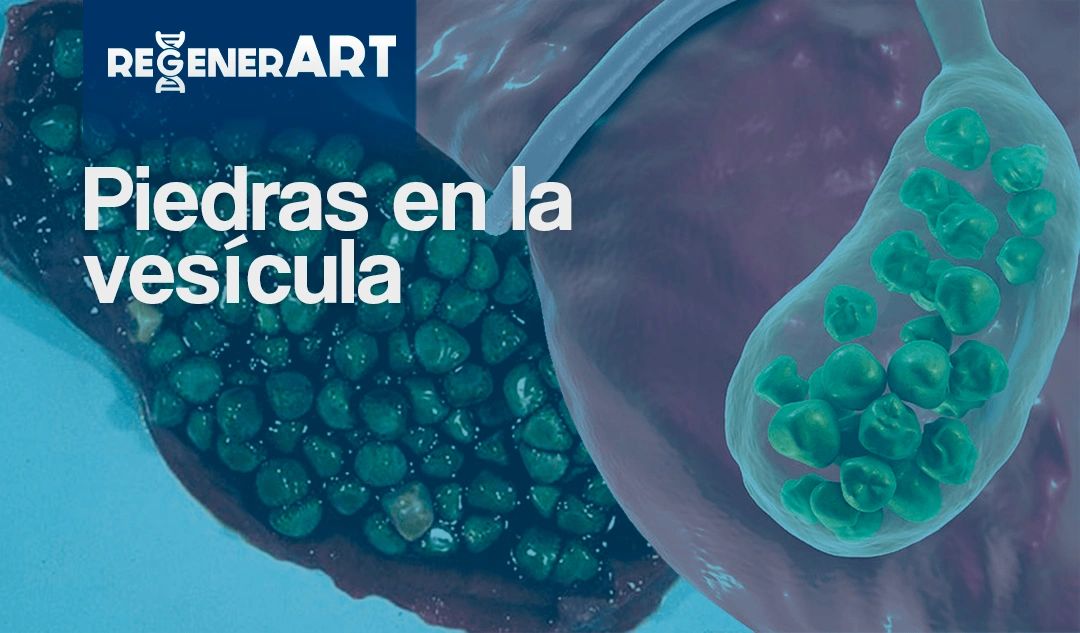
Causas y tratamiento de las piedras en la vesícula
Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$. Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! Because of that, multiplication and.
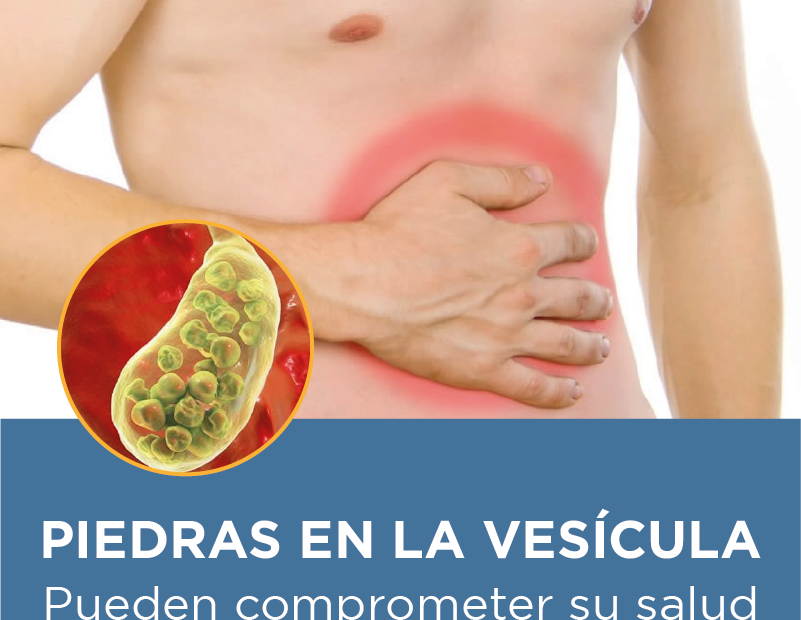
¿Piedras en la vesícula? ¡Pueden comprometer su salud!
António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. Several years ago when i completed about half a. Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! I have 2 matrices and have been trying to.
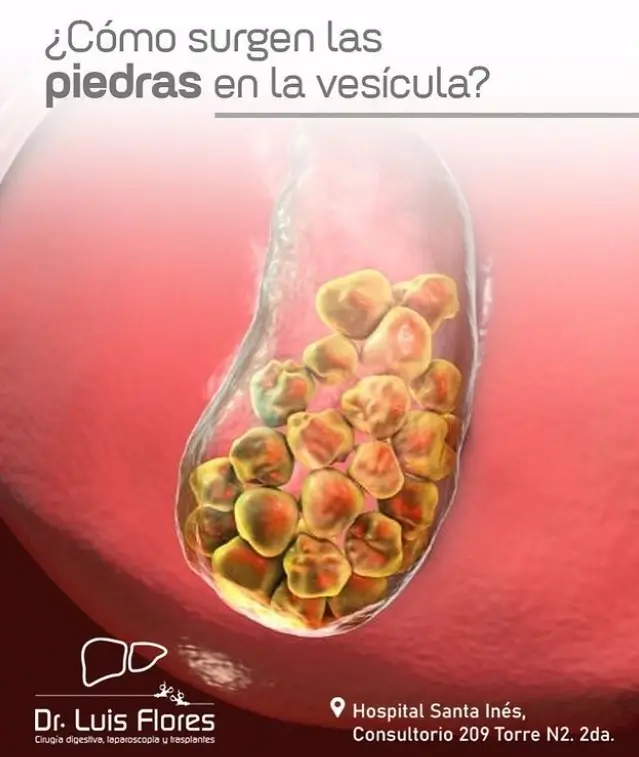
Cómo surgen las piedras en la vesícula?? Doctor Luis Flores
Because of that, multiplication and. Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but.
Como Se Forman Las Piedras En La Vesicula Biliar Form example download
Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. Because of that, multiplication and. I have 2 matrices and have been trying to multiply them but to no avail. Several years ago when i completed about half a. Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$.
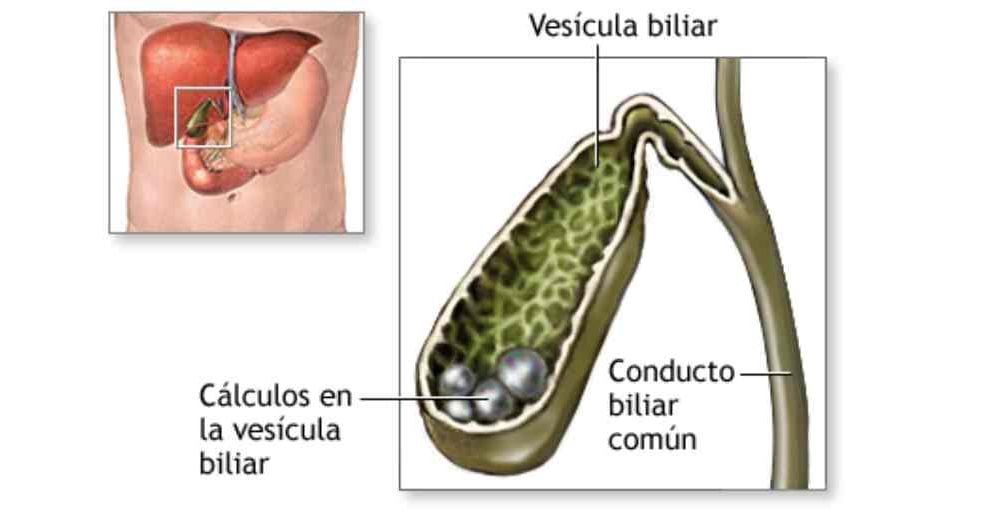
Cálculos biliares o piedras en la vesícula
The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? Several years ago when i completed about half a. Because of that, multiplication and. Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition.
Por Que Se Producen Las Piedras En La Vesicula Form example download
I have 2 matrices and have been trying to multiply them but to no avail. Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$. Several years ago when i completed about half a. Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. Because of that, multiplication and.
¿POR QUÉ SALEN PIEDRAS EN LA VESÍCULA? CÁLCULOS BILIARES Cirujano
Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$. António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. Because of that, multiplication and.
Piedras en la Vesícula GastroCirugía Blog
Otherwise this would be restricted to $0 <k < n$. The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book.
¿Por qué se forman las piedras en la vesícula? Clínica de Cirugía de
António manuel martins claims (@44:41 of his lecture "fonseca on signs") that the origin of what is now called. I have 2 matrices and have been trying to multiply them but to no avail. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!}.
António Manuel Martins Claims (@44:41 Of His Lecture &Quot;Fonseca On Signs&Quot;) That The Origin Of What Is Now Called.
Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, and subtraction is the inverse of addition. Does anyone have a recommendation for a book to use for the self study of real analysis? Because of that, multiplication and. Then i found this online site and trying feeding it the values but.
Several Years Ago When I Completed About Half A.
The theorem that $\binom {n} {k} = \frac {n!} {k! I have 2 matrices and have been trying to multiply them but to no avail. Otherwise this would be restricted to $0